 简单篇
简单篇
# 简单篇
# 1. 两数之和 (opens new window)
# 题目描述

# 方法一:暴力枚举
/**
* 1、暴力枚举 -- 49ms(40.58%), 42.8MB(9.48%)
*/
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
// return new int[]{i, j};
result[0] = i;
result[1] = j;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 方法二:哈希表映射
/**
* 2、哈希表映射 -- 1ms(99.52%), 42.9MB(5.7%)
*/
class Solution2 {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 创建一个HashMap
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果map中包含target - nums[i],则返回map中target - nums[i]对应的值和i
if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
// 将nums[i]和i放入map中
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
// 如果没有找到两个数的和等于target,抛出异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 20. 有效的括号 (opens new window)

class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
// 用数组来做,思想和用栈做一样,但效率高
char[] c = new char[s.length()];
// 标记数组 c 中下一个元素应该插入的位置
int index = 0;
// 遍历字符串 s 中的每个字符
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
// 取出字符串 s 中第 i 个字符
char c1 = s.charAt(i);
if(c1 == '(')
// 如果该字符是左括号 '(', 则将相应的右括号 ')' 存入数组 c 中
c[index++] = ')';
else if(c1 == '[')
// 如果该字符是左括号 '[', 则将相应的右括号 ']' 存入数组 c 中
c[index++] = ']';
else if(c1 == '{')
// 如果该字符是左括号 '{', 则将相应的右括号 '}' 存入数组 c 中
c[index++] = '}';
else if(index == 0 || c[--index] != c1)
// 如果该字符不是左括号,且该字符与数组 c 中最后一个元素不匹配,或者数组 c 中没有元素,则返回 false
return false;
}
// 如果数组 c 中的所有元素都被匹配了,则返回 true,否则返回 false
return index == 0;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
int n = s.length();
if(n % 2 == 1){
return false;
}
int length = n / 2;
for( int i = 0;i < length;i++){
s = s.replace("()","");
s = s.replace("[]","");
s = s.replace("{}","");
}
return s.length() == 0;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
if(s.length() % 2 == 1){
return false;
}
HashMap<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put('(',')');
map.put('[',']');
map.put('{','}');
char[] arr = new char[s.length()];
int idx = 0;
for (char c: s.toCharArray()) {
if (map.containsKey(c)) {
arr[idx++] = c;
continue;
}
if (idx == 0) {
return false;
}
if (map.get(arr[idx-1]) == c) {
idx--;
} else {
return false;
}
}
return idx == 0;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 21. 合并两个有序链表 (opens new window)
# 题目描述

# 方法一:迭代
/**
* 1、迭代(双指针) -- 0ms(100.00%), 41.5MB(5.14%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(m + n), 其中 m 和 n 分别为两个链表的长度。
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode res = new ListNode();
ListNode curr = res;
// 均不为 空 的情况
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
curr.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
curr.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
// 至少有一个为 空 的情况
curr.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
return res.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 方法二:递归
/**
* 2、递归 -- 0ms(100.00%), 41.62MB(5.14%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(m + n), 其中 m 和 n 分别为两个链表的长度。
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(m + n)
*/
class Solution2 {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
} else if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
} else if (list1.val < list2.val) {
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
} else {
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
先递归,再回溯 return
# 70. 爬楼梯 (opens new window)

// 动态规划
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
// 001 011 112 123 235
int a = 0, b = 0, res = 1;
for(int i =1; i <= n; i++) {
a = b;
b = res;
res = a + b;
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 94. 二叉树的中序遍历 (opens new window)
# 题目描述
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
2
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
2
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
2
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
# 方法一:递归
/**
* 1、递归 -- 0ms(100.00%), 40.80MB(5.08%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// 新建一个存放遍历结果的集合
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 左根右排序 遍历
midorder(root, res);
// 返回遍历结果
return res;
}
public void midorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
// 判断到空节点,直接断开
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 递归左子树
midorder(root.left, res);
// 存值
res.add(root.val);
// 递归右子树
midorder(root.right, res);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 方法二:栈
/**
* 2、栈 -- 0ms(100.00%), 40.73MB(5.29%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// 创建结果列表,用于存储中序遍历后的值
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 创建一个栈,用于存储遍历过程中的节点
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
// 当根节点不为空或者栈不为空时,循环继续
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// 如果根节点不为空
if (root != null) {
// 将根节点入栈
stack.push(root);
// 继续遍历左子树
root = root.left;
// 否则,弹出栈顶节点,将其值添加到列表中,遍历右子树
} else {
// 弹出栈顶节点
root = stack.pop();
// 将栈顶节点的值添加到列表中
res.add(root.val);
// 遍历右子树
root = root.right;
}
}
// 返回中序遍历后的列表
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# 方法三:莫里斯遍历
/**
* 3、Morris(莫里斯) 实现中序遍历 -- 0ms(100.00%), 40.73MB(5.29%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// 创建结果列表,存放中序遍历的结果
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 有根节点时,进行循环
while (root != null) {
// 如果根节点的左子节点为空,将根节点的值添加到列表中,然后将右子节点作为新的根节点
if (root.left == null) {
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
} else {
// 否则,找到根节点左子树的最右子节点(中序遍历在根节点之前的节点)
TreeNode prev = root.left;
while (prev.right != null && prev.right != root) {
prev = prev.right;
}
// 如果最右子节点的右子节点为空,将其右子节点设置为当前根节点,然后将左子节点作为新的根节点
if (prev.right == null) {
prev.right = root;
root = root.left;
} else {
// 否则(即最右子节点的右子节点为当前根节点),将根节点的值添加到列表中,将最右子节点的右子节点设为空,然后将右子节点作为新的根节点
res.add(root.val);
prev.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
}
// 返回中序遍历的结果
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 图解莫里斯
参考文章:【动画模拟】二叉树神级遍历!(Morris) - 知乎 (zhihu.com) (opens new window)
# 101. 对称二叉树 (opens new window)
# 题目描述
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
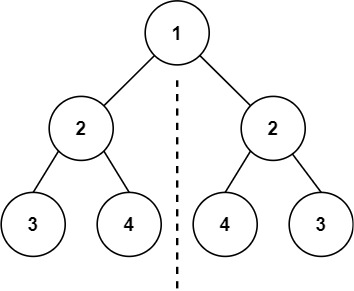
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
2
示例 2:
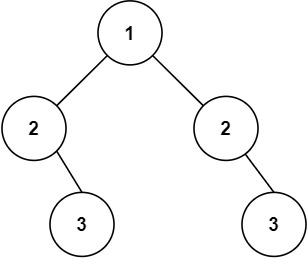
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
2
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
**进阶:**你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
# 方法一:迭代(队列)
/**
* 1、迭代(队列) -- 1ms(19.18%), 40.98MB(5.02%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
queue1.offer(root.left);
queue2.offer(root.right);
while (!queue1.isEmpty() && !queue2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode left = queue1.poll();
TreeNode right = queue2.poll();
if(left == null && right == null){
continue;
}
if(left == null || right == null || left.val != right.val){
return false;
}
queue1.offer(left.left);
queue1.offer(left.right);
queue2.offer(right.right);
queue2.offer(right.left);
}
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 方法二:递归
/**
* 2、递归 -- 0ms(100.00%), 40.89MB(5.02%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n), 因为要遍历 n 个节点
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n), 因为递归需要栈空间, 空间复杂度是递归的深度, 也就是跟树高度有关
*/
class Solution2 {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, root);
}
private boolean dfs(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) {
return true;
}
if (root1 == null || root2 == null || root1.val != root2.val) {
return false;
}
return dfs(root1.left, root2.right) && dfs(root1.right, root2.left);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 104. 二叉树的最大深度 (opens new window)
# 题目描述
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
2
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
2
# 方法一:队列(广度优先搜索)
/**
* 1、队列(广度优先搜索) -- 1ms(22.26%), 41.79MB(5.38%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
// 判断 根节点是否为空
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 建立一个新队列,存每一层的节点
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 根节点进队列
queue.offer(root);
// 深度值计数
int res = 0;
// 循环直到队列为空
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 这一层队列的个数
int size = queue.size();
// 遍历这一层所所有节点并 出队列
while(size > 0) {
// 出队
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 左子树不为空,进队
if(node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
// 右子树不为空,进队
if(node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
size--;
}
// 深度+1
res++;
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 方法二:递归
/**
* 2、递归 -- 0ms(100.00%), 41.63MB(11.64%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 (opens new window)
# 题目描述
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 高度平衡 二叉搜索树。
高度平衡 二叉树是一棵满足「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 」的二叉树。
示例 1:
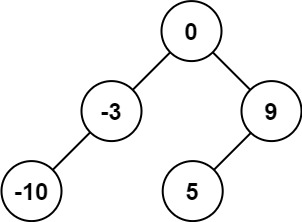
输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
解释:[0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] 也将被视为正确答案:
2
3
示例 2:
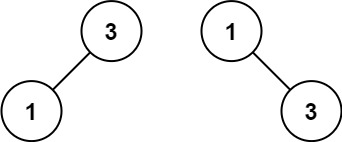
输入:nums = [1,3]
输出:[3,1]
解释:[1,null,3] 和 [3,1] 都是高度平衡二叉搜索树。
2
3
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104nums按 严格递增 顺序排列
# 题目分析
题意:根据升序数组,恢复一棵高度平衡的 BST🌲。
分析:
- BST 的中序遍历是升序的,因此本题等同于根据中序遍历的序列恢复二叉搜索树。
- 因此我们可以以升序序列中的任一个元素作为根节点,以该元素左边的升序序列构建左子树,以该元素右边的升序序列构建右子树,这样得到的树就是一棵二叉搜索树啦
- 又因为本题要求高度平衡,因此我们需要选择升序序列的中间元素作为根节点奥
# 方法一:二分 + 递归
/**
* 1、二分 + 递归 -- 0ms(100.00%), 41.91MB(88.88%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(logn)
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return dfs(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode dfs(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return null;
}
// 以升序数组的中间元素作为根节点 root
// start + (end - start) / 2 == (start + end) >> 1
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
// 递归的构建 root 的左子树与右子树
root.left = dfs(nums, start, mid - 1);
root.right = dfs(nums, mid + 1, end);
// 返回构建好的根节点 root
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
学习参考:
- 108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode) (opens new window)
- 108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - LeetCode Wiki (doocs.github.io) (opens new window)
# 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机 (opens new window)

class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
// 设置起始最小值
int minprice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 最大利润
int maxprofit = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
if(prices[i] < minprice) {
minprice = prices[i];
}else if((prices[i] - minprice) > maxprofit) {
maxprofit = prices[i] - minprice;
}
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 136. 只出现一次的数字 (opens new window)

class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
/*
根据异或性质:
1. 任何数和 0 做异或运算,结果仍然是原来的数,即 a⊕0=a。
2. 任何数和其自身做异或运算,结果是 a⊕a=0。
3. 异或运算满足交换律和结合律,即 a⊕b⊕a=b⊕a⊕a=b⊕(a⊕a)=b⊕0=b。
因此将所有元素进行异或即可得到结果
*/
int res = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
res ^= num;
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
可以利用 Hash 表:
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer i : nums) {
Integer count = map.get(i);
count = count == null ? 1 : ++count;
map.put(i, count);
}
for (Integer i : map.keySet()) {
Integer count = map.get(i);
if (count == 1) {
return i;
}
}
return -1; // can't find it.
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
双循环:
int singleNumber(int* nums, int numsSize){
for(int i=0;i<numsSize;i++){
int count=0;
for(int j=0;j<numsSize;j++){
if(nums[j]==nums[i])
count++;
}
if(count==1)
return nums[i];
}
return -1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 141. 环形链表 (opens new window)
# 题目描述


# 方法一:快慢指针
/**
* 1、快慢指针 -- 0ms(100.00%), 42.80MB(21.80%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode fast = head.next;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 方法二:哈希表
/**
* 2、利用不重复性(HashSet) -- 4ms(13.84%), 43.90MB(5.03%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
public class Solution2 {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 创建一个HashSet,用于存储已经访问过的节点
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while(head != null) {
// 如果HashSet中已经存在当前节点,则说明有环
if(!seen.add(head)){
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 160. 相交链表 (opens new window)
# 题目描述


# 方法一:遍历 + HashSet
/**
* 1、遍历 + HashSet -- 6ms(13.58%), 46.7MB(5.00%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(m + n), 其中 m 和 n 分别是 headA 和 headB 的长度。
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(m), HashSet 存储的是 headA 的所有节点
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
// 先遍历A链表,并把A链表的所有节点加入到哈希集合中
ListNode temp = headA;
while (temp != null) {
hashSet.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
// 再遍历B链表
temp = headB;
while (temp != null) {
// 判断集合中是否包含B链表的此节点
if (hashSet.contains(temp)) {
// 包含,返回相交节点
return temp;
}
// 不包含,遍历下一个节点
temp = temp.next;
}
// 没有相交节点,返回null
return null;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 方法二:双指针
思路分析:
pA遍历 a+c+b 次 pB遍历 b+c+a 次
pA == pB 即可得到相交节点
/**
* 2、双指针 -- 1ms(99.09%), 47.42MB(5.00%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(m + n), 其中 m 和 n 分别是 headA 和 headB 的长度。
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode a = headA, b = headB;
while (a != b) {
a = a == null ? headB : a.next;
b = b == null ? headA : b.next;
}
return a;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 169. 多数元素 (opens new window)

class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer i : nums) {
Integer count = map.get(i);
count = count == null ? 1 : ++count;
map.put(i, count);
}
for (Integer i : map.keySet()) {
Integer count = map.get(i);
if (count > nums.length/2) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 206. 反转链表 (opens new window)
# 题目描述

# 方法一:双指针
/**
* 1、迭代(双指针) -- 0ms(100.00%), 41.18MB(5.01%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n), 其中 n 为链表的长度。
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 假设最前面是个null
ListNode prev = null;
// 当前节点,初始值为头节点。
ListNode curr = head;
// 遍历链表,每遍历一次就转换一次箭头
while (curr != null) {
// 存储当前节点(头节点)的下一节点
ListNode next = curr.next;
// null(prev)->curr 变为 null(prev)<-curr,转换箭头
curr.next = prev;
// 前置指针后移一位
prev = curr;
// 后置指针后移一位
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 方法二:递归
/**
* 2、递归 -- 0ms(100.00%), 41.30MB(5.01%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n), 其中 n 为链表的长度。
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution2 {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 空链表 或者 尾结点
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 递归
ListNode res = reverseList(head.next);
// 反转箭头
head.next.next = head;
// 每一节点指向null,把null放最后
head.next = null;
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 226. 翻转二叉树 (opens new window)
# 题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
2
示例 2:
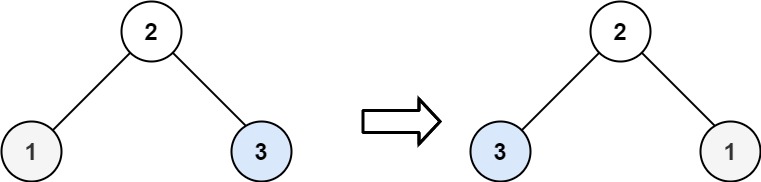
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
2
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
2
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
# 方法一:递归
/**
* 1、递归(DFS) -- 0ms(100.00%), 40.19MB(5.04%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// 递归左子树
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
// 递归右子树
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
// 翻转
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 方法二:队列
层序遍历
/**
* 2、队列(BFS) -- 0ms(100.00%), 40.00MB(17.56%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution2 {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
TreeNode temp = cur.left;
cur.left = cur.right;
cur.right = temp;
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 方法三:栈
/**
* 3、栈(DFS) -- 0ms(100.00%), 40.21MB(5.04%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution3 {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
TreeNode tmp = cur.left;
cur.left = cur.right;
cur.right = tmp;
if (cur.left != null) {
stack.push(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
stack.push(cur.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 234. 回文链表 (opens new window)
# 题目描述

# 方法一:遍历 + 数组
/**
* 1、遍历 + 数组 -- 4ms(79.41%), 55.22MB(84.99%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 空链表或仅包含一个元素的链表无论如何都是回文的(题目描述必定不为空)
// if (head == null || head.next == null) {
// return true;
// }
int len = 0;
ListNode p = head;
// 得出链表长度
while (p != null) {
len++;
p = p.next;
}
// 定义一个与链表一样长的数组
int[] arr = new int[len];
// 重新定义一下链表,因为上面定义的已经为空
p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
arr[i] = p.val;
p = p.next;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[len - 1 - i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 方法二:遍历 + 列表
/**
* 2、遍历 + 列表 -- 8ms(37.68%), 54.37MB(97.42%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (head != null) {
list.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int mid = list.size() >> 1;
for (int left = 0; left < mid; left++) {
if (list.get(left) != list.get(list.size() - 1 - left)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 方法三:快慢指针 + 反转链表
/**
* 3、快慢指针 + 反转链表 -- 4ms(79.41%), 67.43MB(5.6%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
// 使用快慢指针找到链表的中点
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 反转链表的后半部分
ListNode secondHalf = reverseList(slow.next);
slow.next = null;
// 比较前半部分和反转后的后半部分
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = secondHalf;
while (p1 != null && p2 != null) {
if (p1.val != p2.val) {
return false;
}
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return true;
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode current = head;
while (current != null) {
ListNode nextNode = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = nextNode;
}
return prev;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# 283. 移动零 (opens new window)
# 题目描述

# 方法一:位置交换
/**
* 1、位置交换 -- 1ms(99.96%), 44.23MB(16.49%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度分析:由于只对数组进行了一次遍历,所以时间复杂度为 O(n),其中 n 是数组的长度。
* <p>
* 空间复杂度分析:除了输入数组之外,没有使用额外的数据结构来存储信息,因此空间复杂度为 O(1)。
*/
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
// j用来记录非0元素的索引
int j = 0;
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果当前元素不为0
if (nums[i] != 0) {
// 记录当前元素
int tmp = nums[j];
// 将当前元素赋值给非0元素的索引
nums[j] = nums[i];
// 将记录的当前元素赋值给当前元素
nums[i] = tmp;
// 非0元素的索引加1
j++;
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 方法二:新数组拷贝到原数组
/**
* 2、新数组拷贝到原数组 -- 1ms(99.96%), 43.45MB(98.82%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:总的时间复杂度为两个循环的时间复杂度之和,即 O(n + n) = O(2n)。
* 空间复杂度为:由于创建了一个新的数组 arr 来存储非零元素,所以空间复杂度为 O(n),其中 n 是数组的长度。
*/
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int[] arr = new int[nums.length];
int count = 0;
// 遍历数组nums,将非0元素放入新的数组arr中
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
arr[count] = nums[i];
count++;
}
}
// 将新数组arr中的剩余位置都赋值为0
for (int j = count; j < nums.length; j++) {
arr[j] = 0;
}
// 将新数组arr的值拷贝到原数组nums中
// nums = Arrays.copyof(arr,arr.length);
System.arraycopy(arr, 0, nums, 0, arr.length);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 338. 比特位计数 (opens new window)

最高有效位:
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
// 最高有效位
int highBit = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// 判断 i是否是2的幂次方,如果数字i是2的幂次方(10,100),则它的二进制表示中只有最高位是1,其余位都是0
if((i & (i - 1)) == 0) {
// 如果是,更新当前最高位(它的二进制表示中只有最高位是1,其余位都是0)
highBit = i;
}
// 如果当前数字i是2的幂次方,那么它的二进制中1的个数为1;(此时最高位是自己,bits[0] + 1)
// 否则,它的二进制中1的个数等于它去掉最高位1(110 -> 10)后的数字的二进制中1的个数加1
bits[i] = bits[i - highBit] + 1;
}
return bits;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
(i & (i - 1)) == 0是一个位运算的判断条件,它的含义是:如果数字i是2的幂次方,则它的二进制表示中只有最高位是1,其余位都是0。因此,当我们将i与i-1进行按位与运算时,如果结果为0,则说明i的二进制表示中只有一个1,即i是2的幂次方。这是因为,当i是2的幂次方时,i-1的二进制表示中的所有位都是1,因此按位与运算之后得到的结果为0;而当i不是2的幂次方时,i-1的二进制表示中会有一些位是0,按位与运算之后得到的结果就不为0。 在这段代码中,我们使用这个条件来判断当前数字i是否是2的幂次方,如果是,则更新当前的最高位为该数字;否则,根据上述算法计算当前数字的二进制中1的个数。因此,这个判断条件在这个算法中起到了很重要的作用。
class Solution { public int[] countBits(int n) { int[] bits = new int[n + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { bits[i] = bits[i >> 1] + (i & 1); } return bits; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9这也是一个计算数字0到n的二进制中1的个数的算法,具体来说,我们可以通过位运算来计算每个数字的二进制中1的个数。具体来说,对于一个数字i,我们可以将其右移一位,并将结果赋值给bits[i],然后再判断i的二进制表示中的最低位是否为1,如果是,则将bits[i]加1。例如,对于数字6(二进制表示为110),我们将其右移一位得到3(二进制表示为11),此时bits[6]的值为bits[3]的值;然后我们再判断6的二进制表示中的最低位是否为1,发现是,因此需要将bits[6]加1,最终bits[6]的值为2。 这个算法的时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(n)。需要注意的是,这个算法比上一个算法要更加简单和高效,因为它不需要使用特殊的判断条件,而是直接使用位运算来计算每个数字的二进制中1的个数。
# 448. 找到所有数组中消失的数字 (opens new window)

class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for(int num : nums) {
// 计算当前数应该出现的位置,并将该位置的数加上n
int x = (num - 1) % n;
nums[x] += n;
}
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 如果某个位置的数小于n,则说明该位置对应的数字没有出现过
if(nums[i] <= n) {
res.add(i + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 461. 汉明距离 (opens new window)

最低位:
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int s = x ^ y, ret = 0;
while(s != 0) {
// 累积最低位
ret += s & 1;
// 右移一位
s >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Interger.bitCount():
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
return Integer.bitCount(x ^ y);
}
}
2
3
4
5
bitCount实现的功能是计算一个(byte,short,char,int统一按照int方法计算)int,long类型的数值在二进制下“1”的数量
# 543. 二叉树的直径 (opens new window)
# 题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点,返回该树的 直径 。
二叉树的 直径 是指树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的 长度 。这条路径可能经过也可能不经过根节点 root 。
两节点之间路径的 长度 由它们之间边数表示。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:3
解释:3 ,取路径 [4,2,1,3] 或 [5,2,1,3] 的长度。
2
3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2]
输出:1
2
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 104]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
# 方法一:递归
/**
* 1、递归 -- 0ms(100.00%), 41.93MB(5.15%)
* <p>
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* <p>
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
class Solution {
// 全局变量,统计路径节点数
int res;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
// 二叉树的直径(最长路径上的节点数)
res = 1;
// 计算子树的深度
depth(root);
// 节点数 - 1 为边数
return res - 1;
}
// 定义一个方法 depth 用来求二叉树的最大深度
public int depth(TreeNode node) {
// 访问到空节点了,返回0
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
// 当前节点的左子树的深度
int L = depth(node.left);
// 当前节点的右子树的深度
int R = depth(node.right);
// 更新 ans 的值,以找到最长路径上的节点数
res = Math.max(res, L + R + 1);
// 返回当前节点的深度。
return Math.max(L, R) + 1;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# 617. 合并二叉树 (opens new window)

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null) {
return root2;
}
if (root2 == null) {
return root1;
}
// 深度优先搜索
TreeNode merged = new TreeNode(root1.val + root2.val);
merged.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left);
merged.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right);
return merged;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
